Event Logging¶
The event logging system implements a data collection facility, which collects events from different sources to filters and limits them in order to store them. For details about the canonical event format see “canonical event format”.
The Event Logging system has the following main goals:
filter events depending on filter settings
limit events to log if a configured limit (logs per time) is exceeded
optimize storage access to minimize IO operations and maximize physical storage lifetime
Motivation:
For the design the following assumptions are made: (TBD make some reliable measurements)
the upper limit of available storage is 100GB
an storage entity the event is round about <= 100Kb
10⁶ events; 100 event/s => 60H
All events are treated equal / categorize events and apply different storage retention policies
What is the minimal expected time frame to hold events (1a ?)
512 Bytes is smallest storage entity size (SSD/MMC always write at least 512 byte)
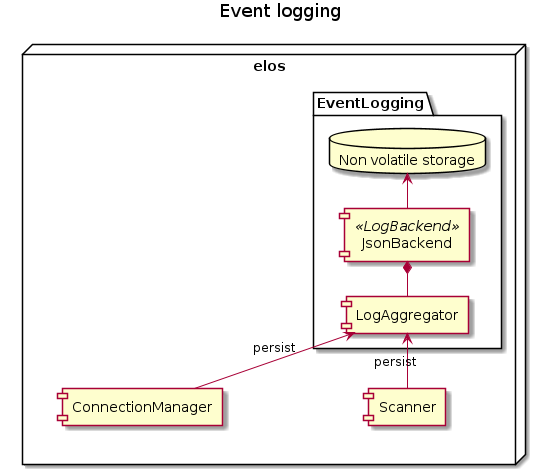
Log aggregation¶
The details on storing events shall be encapsulated by a component called LogAggregator. This component is responsible for the following tasks:
manage storage backend start, stop
filter and limit event logs
forward events to the actual storage backend to persist them
manage concurrent storage requests
manage retention policy, (trigger log cleanup, drop old logs )
monitor storage backend health, generate notification about failing storage backend
manage multiple backends (compile time or as loadable plugin?)
The Loggagregator is a shared instance in the elosd. So it has to synchronize all attempts to persist an event.
Logging Backend(s)¶
The actual storage process depends on the storage engine used. Therefore this is abstracted in so called Storage backends. A storage backend takes one or more events store them in the underlying storage engine. A storage engine could be a simple file write, a database or any other solution that fits the needs for the target system.
The interface of a storage backend consist basically of the following tasks:
Backend open
Backend store
Backend close
Realize required retention policy
The following Design Decision shall describe the decision process for the final storage backend to use.
Design Decision – Storage backend¶
JSON-File based
DBMS - SQLITE
Time series DB
NoSQL
Custom implementation
Fetch API¶
Requirements:¶
Data-source not persistent (In-Memory)
Limits: * Last <n> events per source/per msg-code * Maybe: msg-counter (how many events of this type)
Ensure/Respect the ~65KB message-size-limit of the protocol
Static View:¶
One storage backend provides a read-access to older events to provide the fetchAPI.
The fetchAPI-backend (fab) is a normal storage backend of elos and is loaded and configure as a normal storage backend. Thus the fab only receives events that pass the RPN filter configure to that backend.
The plugin-name of the fab must be „fetchapi“ to be recognised. Thus only one storage-backend-plugin-instance configured with the name “fetchapi” is allowed.
Basic feature of fab: one ringbuffer for all events. The size can be configured.
Advanced feature of fab: tbd
The plug-in is preferred to be written in C++ with a ringbuffer and sync from the stdc++.
Limit fetch result to maintain 65kb protocol limit by providing a Paging-API and indicate to large results with a truncated flag
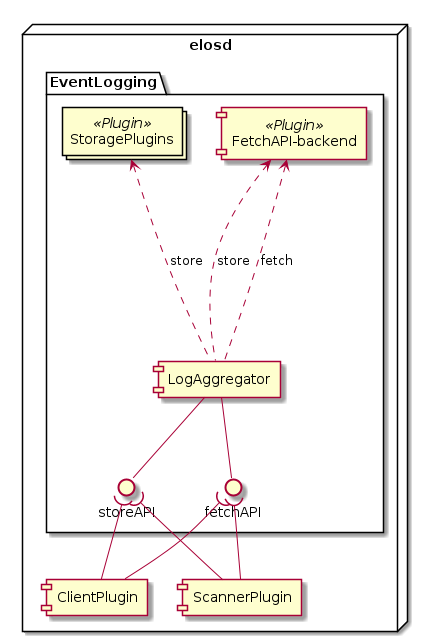
Component overview of the LogAggregator¶
{
"root": {
"elos": {
"EventLogging": {
"Plugins": {
"fetchapi": {
"run": "always",
"file": "inmemory.so",
"Filter": [
"1 1 EQ"
],
"config": {
"size": "1MB"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Dynamic View¶
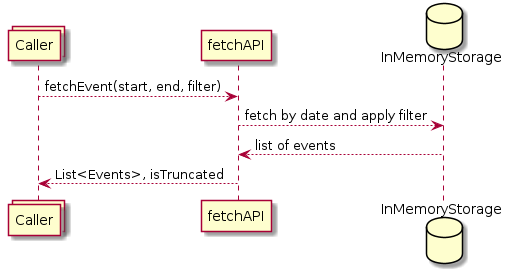
The fetch event process¶