libelos¶
The Library comes in form of a c library (libelos) and a header file. The library provides two APIs :
Event-API:
Used to publish and subscribe to events
LogAggregator-API (DCF-API)
Used to store logs (content of a log see SM_REQ001)
Used to access logs (content of a log see SM_REQ001)
The libelos by default doesn’t log anything to stdout or stderr. Defining the environment variable LIBELOS_LOG with any value libelos will be verbose and print out errors, warnings etc.
Design decision – Thread Safety¶
TBD: The library is intended to be thread safe and forkable, with no worker threads and synchronous input/output.
Actual implementation¶
The functions are documented in this section
There is also a simple sequence diagram available further down below that shows how to interact with the server.
elosEventQueueRemove¶
Removes a previously created EventQueue.
int elosEventQueueRemove(
elosSession_t *session,
elosEventQueueId_t eventQueueId
);
Parameters:
[in]session -> session data structure[in]eventQueueId -> the id for the EventQueue that shall be removed
Returns: * 0 for success or errorcode < 0 on failure
elosEventQueueSetLimit¶
Restrict the amount of events that can be recorded in a given timeframe. This replaces the default values from the configuration file for the specified EventQueueID.
int elosEventQueueSetLimit(
elosSession_t *session,
elosEventQueueId_t eventQueueId,
struct timespec timeframe,
uint32_t events
);
Parameters:
[in]session -> session data structure[in]eventQueueId -> the id for the EventQueue that shall be modified[in]timeframe -> the timeframe in which the maximum amount of events can occur[in]events -> the maximum amount of events that can occur in the specified timeframe
Returns: * 0 for success or errorcode < 0 on failure
elosEventQueueGetLimit¶
Fetch the amount of events that can be recorded in a given timeframe,
these are either the default values from the configuration file or the
values set by the last elosEventQueueSetLimit() call.
int elosEventQueueGetLimit(
elosSession_t *session,
elosEventQueueId_t eventQueueId,
struct timespec *timeframe,
uint32_t *events
);
Parameters:
[in]session -> session data structure[in]eventQueueId -> the id for the EventQueue that shall be modified[out]timeframe -> the timeframe in seconds in which the maximum amount of events can occur[out]events -> the maximum amount of events that can occur in the specified timeframe
Returns: * 0 for success or errorcode < 0 on failure
elosLogFilterCreate¶
Creates a logFilter struct that can contain one or more rules for filtering log entries from the database during a read.
int elosLogFilterCreate(
elosSession_t* session,
logFilter_t *logFilter,
);
elosLogFilterAddRule¶
Adds a new filter rule to the logFilter struct.
int elosLogFilterAddRule(
elosSession_t* session,
logFilter_t *logFilter,
logFilterRule_e logFilterRule, // <TBD> e.g. LOG_FILTER_RULE_TIMESTAMP
const void* logFilterParam // <TBD> e.g. a struct with timestamp values
);
elosLogFilterDestroy¶
Frees the memory associated with a logFilter struct.
int elosLogFilterDestroy(
elosSession_t* session,
logFilter_t *logFilter,
);
elosLogFindEvent¶
Fetches all logged events based on the used filter (e.g. based on payload or other data).
In case no events are in the log, the vector parameter won’t be changed.
The memory of the event vector will be allocated by the library and must be freed afterwards with elosEventVectorDelete().
int elosLogFindEvent(
elosSession_t *session,
const char *filterRule,
elosEventVector_t **vector
);
Parameters:
[in]session -> session data structure[in]filterRule -> filter rule for entry selection[out]vector -> list of event structs
Returns: * 0 for success or errorcode < 0 on failure
JSON data structure example¶
Each event will always have the fields name, timestamp, and data
The data field is individual for each event type, they will be described in a separate section of this document.
{
"events": [
{
"name": "COREDUMP_STARTED",
"timestamp": 1631720019,
"data": {
"pid": "1234",
"exe": "/usr/bin/crashed_application",
"corefile": "/tmp/coredump_with_identifiers"
}
},
{
"name": "TEMPERATURE_HIGH",
"timestamp": 1631717420,
"data": {
"sensor_1": "71.0",
"sensor_2": "63.7"
}
}
]
}
Example sequence diagram¶
This sequence diagram shows a simplified use case for polling for events.
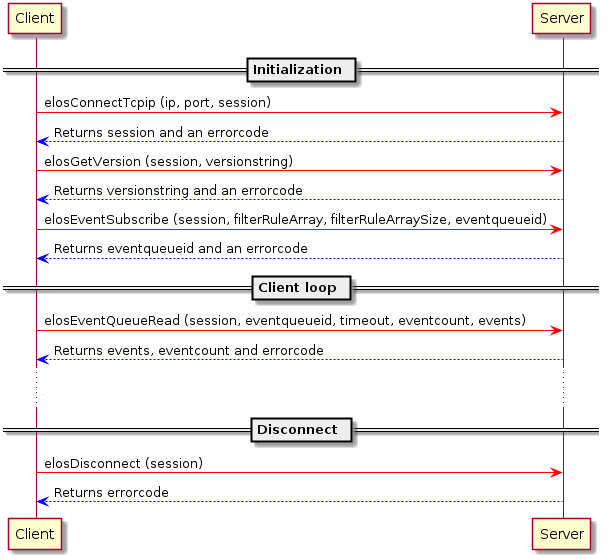
Library sequence diagram¶