Kernel development
If you do the bring-up for a new board, you may need to adapt the kernel configuration. This section continues where “Building an image from scratch” ended.
Please be aware that EB corbos Linux allows you to “open the box”, but if you modify the provided binary packages the support and maintenance for these packages is not covered with the base offer. You can get support, qualification and long term maintenance as an add-on to the base offer, as a yearly fee for each package.
Nevertheless, let’s see how we can build our own kernel. To build a custom kernel package we need the kernel sources and the base kernel config. We can get the kernel sources and build dependencies using apt:
mkdir -p kernel
cd kernel
apt -y source linux-buildinfo-5.15.0-1034-s32-eb
sudo apt -y build-dep linux-buildinfo-5.15.0-1034-s32-eb
For extracting the kernel config, we can again make use of the boot generator:
# Derive values from base.yaml - relative path
base: base.yaml
# Do not pack the files as tar
tar: false
# download and extract the kernel package incl. depends
use_packages: true
# Files to copy to the build folder
files:
- boot/config*
We can copy this config as .config into the kernel source and build the kernel using task.
To make use of our local built kernel binary we need and adapted boot.yaml:
# Derive values from base.yaml - relative path
base: base.yaml
# Reset the kernel value - we don't want to download and extract it
kernel: null
# Do not pack the files as tar
tar: false
# do not download and extract these packages, they are already installed in the boot_root.tar
use_packages: false
# Name of the boot root archive
base_tarball: $$RESULTS$$/boot_root.tar
# Files to copy form the host environment
host_files:
- source: ../bootargs-overlay.dts
destination: boot
- source: ../bootargs.its
destination: boot
- source: $$RESULTS$$/initrd.img
destination: boot
- source: $$RESULTS$$/vmlinuz
destination: boot
# Scripts to build the fitimage and fip.s32
scripts:
- name: ../build_fitimage.sh # Build the fitimage in the boot_root.tar environment
env: chroot
# Files to copy to the build folder
files:
- boot/fip.s32
- boot/fitimage
The only change compared to the old boot.yaml is that we add $$RESULTS$$/vmlinuz to the host_files.
This means our kernel binary is copied to the /boot folder of the fitimage build environment,
and will overwrite the one from the kernel Debian package.
This will give us the following build flow:
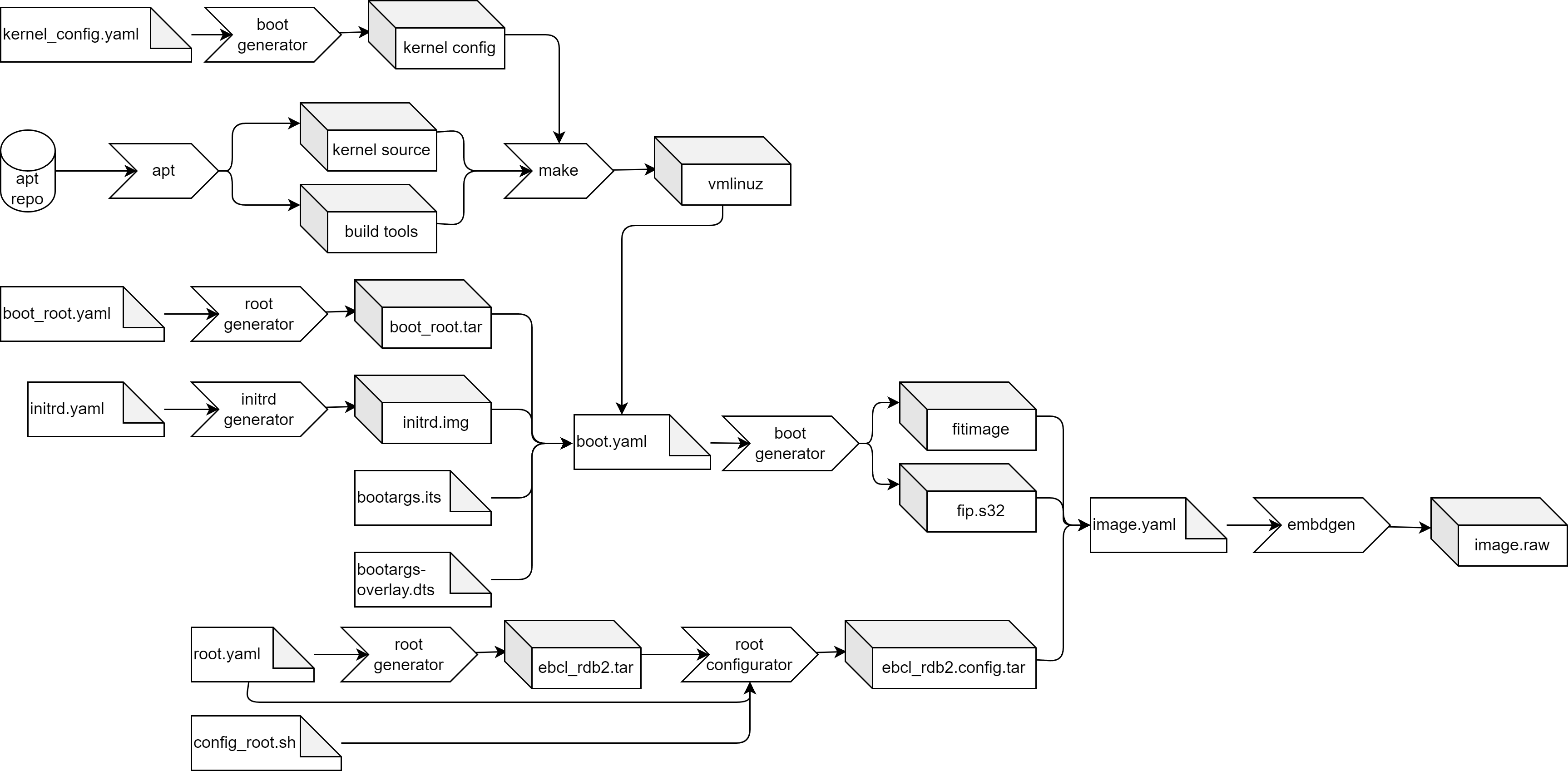
This build flow is implemented in the generic build_with_local_kernel task of images/tasks/RDB2_image.yml.
...
tasks:
...
build_with_local_kernel:
desc: Build NXP RDB2 image using a local built kernel binary from Debian package sources.
vars:
boot_root_spec: '{{.boot_root_spec | default "boot_root.yaml"}}'
boot_tarball: '{{.boot_tarball | default "boot_root.tar"}}'
cmds:
- task: kernel:build
- task: initrd:build
- task: root:build
vars:
root_spec: '{{.boot_root_spec}}'
base_tarball: '{{.boot_tarball}}'
- task: boot:build_fitimage
- task: root:build
- task: root:config
- task: embdgen:build
method: none
The additional steps for downloading the kernel sources and building the kernel locally are implemented in images/tasks/Kernel.yml.
...
tasks:
build:
desc: Build kernel form Debian package sources.
vars:
result_folder: '{{.result_folder | default "./build/"}}'
base_spec: '{{.base_spec | default "base.yaml"}}'
kernel_config: '{{.kernel_config | default "kernel_config.yaml"}}'
kernel: '{{.kernel | default "vmlinuz"}}'
cmds:
- task: source
- task: kconfig
- task: build_kernel
- task: build_modules
preconditions:
- test -f {{.kernel_config}}
sources:
- '{{.base_spec}}'
- '{{.kernel_config}}'
generates:
- '{{.result_folder}}{{.kernel}}'
...
The build task of images/tasks/Kernel.yml:
- Downloads the kernel sources, and installs the build dependencies in the container.
- Extracts the kernel configuration from the binary Debian kernel package, and updates the config.
- Builds the kernel binary,
- and builds the kernel modules.
For more details, please take a look at the file.